Department Events
Guidance session on “Curriculum Design” on 22/12/2023
The Department has organized
a guidance session by Dr. B. N. Chaudhari for all the faculty members of
the Electrical Department on ‘Curriculum Design’ on 22nd December 2023. He
explained the same with the help of chalk and duster in a systematic manner and
guided everyone. He emphasized the role of teachers in making the
teaching-learning process joyful and meaningful.
Session on ‘Curriculum Design in the View of NEP 2020’ on 21/12/2023
The department has organized the session of Dr B. N. Chaudhari, Principal, Sardar Patel Institute of Technology, Mumbai on 21st December 2023 for all the faculty members of the institute on ‘Curriculum Design in the View of NEP 2020’. The session was very interesting and interactive. All the faculty members enjoyed the session. The strong message was to work hard to make the successful implementation of NEP at the institute.
Industry Leaders Summit 3.0 (Round Table Discussion) on 14/12/2023
The K.K.Wagh Institute of Engineering Education &
Research has organized an Industry
Leaders’ Summit 3.0 (Round Table Discussion) on 14th December 2023. All the
industry leaders from the Nashik region joined for this summit. From the
Department Prof. Dr. Ravindra Munje, Dr
Sharad Dhamal, Prof. Nayana Jangle, Prof. Sudhir Shinde, Prof. Ganesh Jadhav,
Prof. Rupali Ahire and Prof. Saravanan.S represented the Electrical
Engineering Round tables.
CEO Meeting Round Table Discussions
The K.K.Wagh Institute of Engineering Education &
Research has organized an 'Industry
Leaders Summit 3.0' on 14th December 2023 and invited all the Industry
Leaders in the Nashik region. One of the round tables coordinated by the
department was with Shri. Ganesh
Kothawade, Senior Vice President - ABB India, Shri. Deepak Patil, COO Legrand
(India) Group, Shri. Prashant Kavate and Young Leader Arya Mishra. The team selected the theme of Economic
Outlook and Industry Forecast. The discussion was fascinating and resulted in
several indicative points to implement. Thanks to all of them for being with us
and giving suggestions. The table was coordinated by Dr. Ravindra Munje, Prof. Ganesh Jadhav and Prof. Rupali Ahire.
CEO Meeting “Round Table Discussions”
The K.K.Wagh Institute of Engineering Education &
Research has organized an 'Industry
Leaders Summit 3.0' on 14th December 2023 and invited all the Industry
Leaders in the Nashik region. One of the round tables coordinated by the
department was with Shri. Deepak
Kumthekar, Chief Engineer, Maha discom, Nashik and Shri. Sanjeev Bhole, Chief Engineer, Maha Transco, Nashik. The
discussion was fascinating and resulted in several indicative points to
implement in teaching and learning. Thanks to all of them for being with us and
giving suggestions. The table was coordinated by Prof. Sudhir Shinde.
CEO Meeting Round Table Discussion
The K.K.Wagh Institute of Engineering Education &
Research
has organized an 'Industry Leaders
Summit 3.0' on 14th December 2023 and invited all the Industry Leaders in
the Nashik region. One of the round tables is coordinated by the department.
The discussion was fascinating and resulted in several indicative points to
implement in teaching and learning and curriculum design. Thanks to all of them
for being with us and giving suggestions. The table was coordinated by Dr. Sharad Dhamal and Prof. Nayana Jangle.
National Level Students Conference on ‘AI, ML and IoT Applications in Electrical Engineering’ from 29th- 30th December 2023
Department of Electrical Engineering in association with IET
Nashik Local Network and EFFECT Student Body of the Department has conducted a “National Level Students Conference on ‘AI,
ML and IoT Applications” in Electrical Engineering’ from 29th December to
30th December 2023. A total of 25 research papers are received for the
conference. The Chief Guest and the keynote session speaker for the conference
was Shri. Vimal Chaubey (Data
Engineer at Tata Croma and Chairman of IET Mumbai Local Network). He delivered a talk on Wired for Innovation:
AI, ML, and IoT Transformations in Electrical Engineering for all the students
and participants. Dr. Shubra Jyoti
Sarkar and Dr. Abhishek were the
session chairs for the conference. During the valedictory function, Dr Shubra Jyoti Sarkar presented his
views on the overall conference and guided all the students to write
good-quality research papers. The first prize was given to Yashraj Desale (K.K. Wagh Institute of Engineering Education and
Research), the second prize was given to Nitin
Shejwal (Sanjivani College of Engineering) and the third prize was given to
Kishori Bhadgujar, Viraj Jadhav and Gayatri Desale (K. K. Wagh Institute of
Engineering Education and Research). The conference was well-organized by Prof. Nayana Jangle and Prof. Snehal Sagare.
Expert Session by Shri. Vimal Chaubey
Keynote session by Shri.
Vimal Chaubey (Data Engineer at Tata Croma and Chairman of IET Mumbai Local
Network) at the National Level Students Conference on 'AI, ML and IoT
Applications in Electrical Engineering' on 29th December 2023 at the
Department.
Celebration of ‘Know Our Department’ and ‘Know Our Colleague’ on 07/12/2023
After the term end of all the classes, celebrated for ‘ Know Our Department’ and ‘Know Our Colleague’ on 07/12 /2023. In the first activity of Know Our
Department, a quiz of 40 questions on the K. K. Wagh Education Society, K.K. Wagh Institute of Engineering Education &
Research,
and ElectricalKKWIEER was conducted for all the faculty
members through the Google form. This was an open-book type of quiz. All the
faculty members enjoyed the quiz. In the
second activity for ‘Know Our
Colleague’, faculty and staff members were requested to introduce himself
or herself from a family background point of view and other faculty members
were requested to describe him or her in one adjective. Overall, it was great
fun. Lunch was served during this activity for all the faculty and staff
members.

Student Corner
Student Placement
The following students are placed in various multinational companies. Congratulations to all the students!
Placed
Students Details (December- 2023)
|
Sr. No. |
Name of the Student |
Package |
Placement Date |
| 1 |
Harshal Rajaram
Gaikwad |
5 LPA |
21/12/2023 |
| 2 |
Prathamesh Vinayak
Gaikwad |
5 LPA |
21/12/2023 |
Industrial Visit on 04/12/2023
Industrial Visit on 4th and 5th of December 2023
The Department has conducted an Industrial Visit for S.Y.
B.Tech (Div A) students on the 4th and 5th of December 2023 at RISHABH
INSTRUMENTS LIMITED, Nashik. The visit was coordinated by Prof. Aishwarya Awhad
and accompanied by Mrs. Shubhada Borade
and Ms. Ranjana Gaikwad.
Faculty Corner
Faculty Participation
Dr.
Subhra J Sarkar, Associate Professor from the Department has presented a research paper
at the 3rd International Conference on Emerging Frontiers in Electrical and
Electronic Technologies (ICEFEET- 2023) at NIT Patna on 22nd December 2023 on
the topic 'Investigation of the performance of Resumable Load Data
Compression Algorithm for Distributed Voltage and Frequency Monitoring Data'.
The Annual General Meeting and Elections for the IET India Nashik Local Network are conducted on 23rd December 2023 at Hotel Grant Rio, Nashik. In this AGM, Prof. Sudhir Shinde and Prof. Nayana Jangle are elected respectively as Vice-Chairman and Secretary of the IET Nashik Local Network for 2024. Congratulations to both of them!
Alumni visit to the department on 30/12/2023.
An enthusiastic, energetic and dynamic personality, the president of the IET Karma veer Expo of that time, Mr. Pratham Nigam visited the department on 30th December 2023 and shared his excitement about the upcoming IET Karma veer Expo 2024.
News Paper
Student Articles
The rapid electrification of
the transportation sector is driving car manufacturers to electrify their
fleets with carbon-neutral technologies. Power electronics, a pivotal component
in this shift, is undergoing significant development to meet the reliability
demands of electric and hybrid vehicles (EVs and HEVs). This article delves
into the reliability requirements and challenges of power electronics in EV/HEV
applications, highlighting advances in components that enhance overall system
reliability. It explores a reliability-oriented design methodology through
examples like EV onboard chargers and drive train inverters. While many
reliability aspects are well-handled, the article emphasizes the ongoing need
to address challenges arising from the introduction of new technologies in the
field of power electronics for EVs and HEVs.
1. Introduction
The electrification of modern society is progressing rapidly, driven by a need for efficiency, sustainability, and reduced carbon emissions. Power electronics technology plays a pivotal role in this evolution, particularly in the electrification of the transportation sector. Countries like Norway and Denmark have set ambitious goals for carbon emission-free vehicles, and Bloomberg predicts a substantial increase in electrified car sales by 2040. Power electronics are crucial in electric and hybrid vehicles, contributing to various components such as the drive train and battery management system. The article underscores the importance of modern reliability engineering methods to ensure safety and minimize operational costs. It highlights the challenges associated with wear-out failures in power semiconductor devices and capacitors, emphasizing the need for innovative design and testing methods to enhance the reliability of power electronic systems in the evolving landscape of electrified transportation.
2. System Overview
The integration of power electronics in
electric vehicles (EVs) marks a crucial step in the evolution of sustainable
transportation. This overview underscores the significance of power electronic components,
including inverters, converters, and motor drives, in efficiently converting
electrical energy and powering EVs. The discussion highlights the ongoing
efforts to optimize efficiency, manage thermal challenges, and enhance overall
system performance. The subsequent system description provides insights into
key components like inverters, converters, and motor drives, emphasizing their
roles in influencing the efficiency and reliability of EVs. The comprehensive
coverage extends to aspects such as battery charging, grid integration, fault
diagnosis, and adherence to safety standards, illustrating the intricate
interplay between power electronics and the trajectory of electric vehicle
technology. This concise overview captures the pivotal role of power
electronics in driving the sustainability and future prospects of the electric
vehicle industry.
The passage provides a comprehensive overview of the power electronics
architecture in electric and hybrid vehicles (EV/HEV). It emphasizes the
pivotal role of power electronics at various levels, illustrating a typical
electrical power system in EVs with a focus on key components such as the
high-voltage (HV) and low-voltage (LV) DC buses. The onboard charger (OBC) is
highlighted for its dual function in battery charging and power factor
correction. Challenges related to OBC, including charging time and the demand
for higher-power chargers, are discussed.
(a)
(b)
Fig.2 Block diagram of OBC
and dc–dc converters. (a) Single-phase ac/dc with interleaved boost PFC topology. (b) Isolated dc-dc.
The text introduces isolated dc–dc converter topologies, emphasizing the
use of resonant-based converters like the phase shift full bridge (PSFB) for
improved efficiency. The discussion extends to electric machines (EM) and their
inverters, noting advancements in permanent magnet (PM) EMs and reliability
challenges associated with higher power cycling. The passage concludes with
insights into power-switching devices, including the transition from
insulated-gate bipolar transistors (IGBTs) and silicon MOSFETs to wide bandgap
(WBG) devices like silicon carbide (SiC) and gallium nitride (GaN) for enhanced
efficiency and reduced system size, exemplified by Tesla's adoption of SiC
devices.
4. Power Modules
Advancements in wide
bandgap semiconductor materials and power module packaging are pivotal for
realizing the roadmap towards more efficient electronic systems, particularly
in automotive applications. Silicon Carbide (SiC) MOSFETs, although offering
improved performance, face challenges in power cycling capability compared to
traditional Si IGBTs. To address this, advanced packaging concepts, including
innovative interconnection, substrate, and die-attach elements, are proposed to
enhance reliability and high-temperature operation.
Fig.3
Advances in packaging elements for power modules
The next-generation
automotive modules are expected to operate at temperatures up to 175°C, necessitating
low thermal resistance materials such as AlN and Si3N4 ceramics. Techniques
like heavy copper wire bonding and direct lead bonds are explored to mitigate
bond wire-related failures. Optimized packaging structures, such as over-mould
structures and advanced cooling systems like direct liquid cooling, contribute
to modularity, reduced size, and enhanced performance. Robust testing methods
and standards play a crucial role in ensuring the reliability of these emerging
technologies.
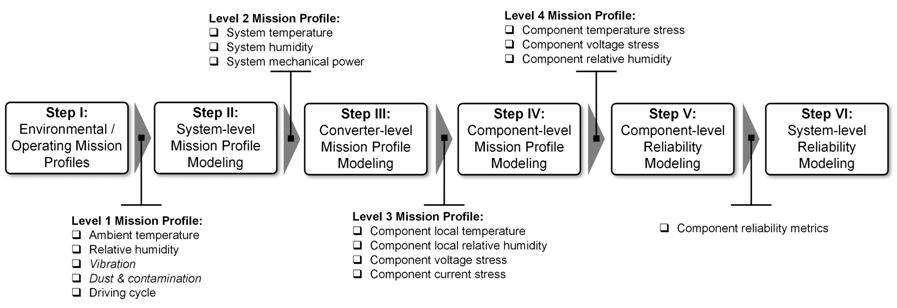
6. Concepts of Mission-Profile-Based Design of Power Electronics
(i) Paradigm Shift: Transition from statistics-based reliability evaluation to Physics of Failure (PoF)-based lifetime estimation in power electronics.
(ii) PoF
Concept: Understanding root
failure causes and mechanisms modeled under realistic operating conditions.
(iii) Empirical
Models: PoF models for
microelectronics are often not scalable for power electronics, leading to the
use of empirical lifetime models.
(iv) DfR
Method: Design for Reliability
(DfR) methods ensure reliability and quality during early product development
stages.
(v) Mission-Profile-Based
Assessment: Procedures integrating
DfR and PoF principles successfully applied in various applications like wind
power converters and electric aircraft.
(vi) Focus
on EV/HEV Applications:
Reliability assessment methodology focuses on power module reliability within
the electrical drive train inverter.
(vii) Six-Step
Lifetime Estimation Procedure:
Comprehensive process evaluating both component and system-level reliability,
requiring extensive knowledge of mechanical, electrothermal, and lifetime
parameters.
(viii) Input
Mission Profiles: Derived from vehicle
driving cycles and ambient temperatures, serving as the basis for reliability
assessments.
(ix) Electromechanical
and Electrothermal Modeling:
Utilized to convert input mission profiles into mechanical power and determine
voltage and current loadings of power electronic components.
(x) Reliability
Metrics: Thermal and electrical
stressors, along with empirical lifetime models, are used to estimate vital
reliability metrics (e.g., lifetime distribution and unreliability curve) of
power electronic components.
(xi) System-Level Reliability: Achieved through a reliability block diagram (RBD) analysis, merging individual component reliability information
Fig.4 General mission-profile-based
reliability assessment procedure for power electronic system.
7. Conclusion
Electronics plays a crucial role in Electric Vehicles (EVs) and Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs), with design and implementation being essential factors. Reliability stands out as a critical success criterion for widespread adoption. The article provides an extensive overview of power electronic architectures in EVs/HEVs, emphasizing the importance of reliability requirements. While some standards exist, others are yet to be defined, indicating ongoing challenges as technology evolves. Component development, especially concerning capacitors and active devices, along with effective cooling, is vital for system reliability and safety. At the system level, a reliability-oriented design is key for cost reduction and optimization, complemented by condition monitoring in operational EV/HEV fleets. Multidisciplinary simulation tools are crucial for Design for Reliability (DfR), illustrated through two case studies. Future challenges and research opportunities include the wider use of wide bandgap devices, enhanced overall system control based on reliability indexes, improved packaging technologies, and dynamic handling of large data for proactive preventive maintenance.